This page correlates with Unit 3 in our book and focuses on circuits, gates and chips
Good websites on this unit’s topics
- Computer Hope, has a lot of general computer /tech things including lots on hardware
A Great Discussion at Quora about the question “What do low level programmers know that high level ones don’t? This discussion helps explain reasons to better understand how hardware and OS concerns do affect programmers.
Logic Gates
- Introduction to Logic gates via MineCraft you tube video
- How the logic gate actually work (hardware..at about 3:00 mins but watch the first 5:00 minutes. I don’t really like the explanation of adding binary numbers but the logic gates are, I think, well explained)
- Mincraft continued (xnor etc..)
- Logic Gate Simulator (create logic gates using online Flash simulator)
- How does a CPU work ? (notice it’s all about logic gates)
- Further reading (not necessary but could be helpful)
Circuits
- Combinational Circuits
- adders, multiplexers
- Circuits as memory
CPU Chapter 5
- You should be familiar with the term accumulator
- Fetch Execute Cycle
- Addressability
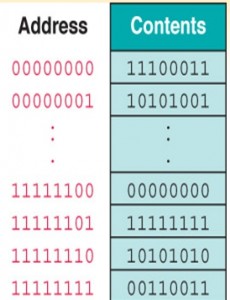
- What is the addressability of the architecture in the pic on the right?
- FSB
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n7jdjEuyljs Good animation of FSB and how its speed affects computer processing
- FSB/Clock ratio
- CPU/ALU
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8LOnlxFITys Broad strokes of the processor’s front side bus, the cpu speed, and what multi core means. This is very non-technical, but gives some good real world analogies for how these things work.
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qiTt33_3boI
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cNN_tTXABUA CPU explained -very techincial and specific. Though parts of this is beyond the scope of the class, it sheds some good light on how RAM and CPU interect
- Cpu explained via logic gates (beyond scope of IB and class but interesting)
- RAM
- Mario, bits and RAM
- Ram Speed : http://mrmonline.org/computer-hardware/

- Caches, RAM and memory
- 32 bit vs 64 bit link #1 Good overview of the topic
- You tube video on 32 vs 64 This disucsses the issue but with more of a slant towards how it affects modern day computers (gaming etc..)
- http://dis-dpcs.wikispaces.com/2.1.4+Machine+Instruction+Cycle
ALU ( The arithmetic logic unit) Chapter 5, p. 128
Computing Components
Stored-Program Concepts
- Raid vs Sata Drives 5.1
- Front Side Bus and othe rparts of computer 5.1
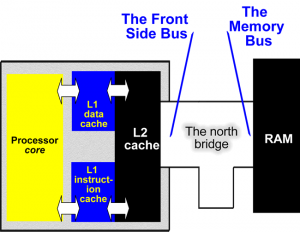
- Von Neumann Architecture
- Fetch-Execute-Cycle
- Ram and ROm
- Secondary Storage
Embedded Systems
Parallel Architectures