Monthly Archives: October 2021
Array Fun 2 [2023]
Complete all the methods below. When you are done, copy and paste the testmethods.v5.1 into your class and run it to see if you have any obvious errors. The above code does not guarantee you a 100 but will help catch most of the common errors that students make.
Note: You may not use any external libraries (like Java.Arrays etc )or import any code. Everything can be done with just loops and variables.
int sumEveryN(int[] nums, int n)
Description:This method returns the sum of every n elements of nums ..
| Method Call | return value/output |
| sumEveryN( {1 , 2 , 3 , 4 }, 2 ) | 4( ie 1 +3) |
| sumEveryN( {13 , 42, 15, 33 , 44 , 16 , 52} ,3) | 98 ( ie 13 + 33+ 52) |
String[] doubleArr(String[] strs)
Description: This method returns a new version of strs in which each element now appears twice. This can be done with a for-each loop, which I believe is easier and more intuitive.
| Method Call | return value/output |
| doubleArr( {“a”,”b”,”c”} ) | {“a”,”a”,”b”,”b”, “c” , “c”} |
| doubleArr( {“math”,”ware”,”house”,”.com” }) | {“math”,”math”,”ware”,”ware”,”house”,”house”,”.com”, “.com”} |
int indexOf5(int[] nums )
Description:This returns the index of the first occurrence element 5 or -1 if 5 does not appear anywhere in the array.
| Method Call | return value/output |
| indexOf5( { 2 , 3 , 5 , 4 } ) | 2 |
| indexOf5( { 2 , 3 , 5 , 4, 5 } ) | 2 |
| indexOf5( { 2 , 3 ,7 , 4, 3, } ) | -1 |
More Sample calls and return vals
int indexOf(int[] nums, int num)
Description: This method returns the index value of the first appearance of num or -1 if num is not an element of nums .
| Method Call | return value/output |
| indexOf( {6,4 ,7,3, 4 }, 4) | 1 |
| indexOf( {6,4 7 ,3,2,7}, 7) | 2 |
| indexOf( {6,4 ,2,3}, 22) | -1 |
int[] randos(int start, int end, int howMany)
Description: This method returns an array of random numbers between [start,end] . Note make sure that each element in the new array attempts to make a new random int. Use Math.random() , do not use any other mechanism for finding a random number.
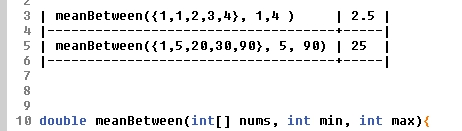
double meanBetween(int[] nums, int min, int max)
Description: This method returns the mean of nums ; however, this method only counts values within the range (min,max) as shown in the examples below:
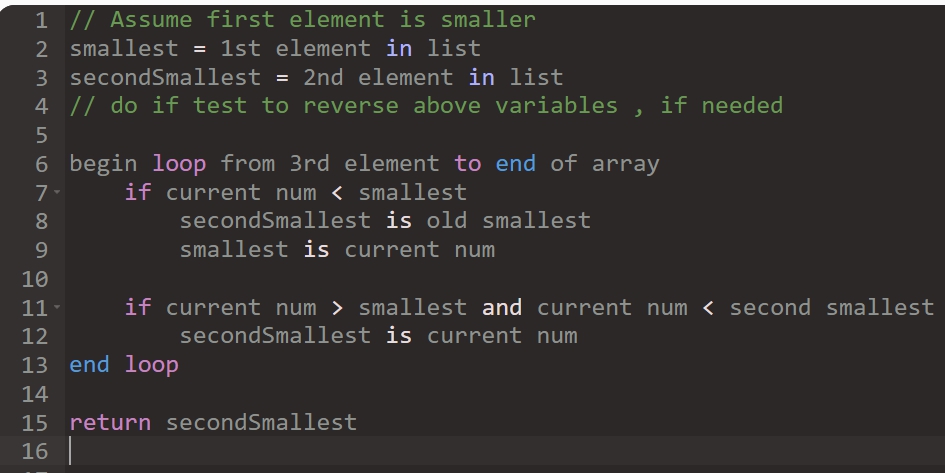
int secondSmallest(int[] nums )
Description: This method returns the element of nums with the second smallest value.
Note: You may not modify the input array. For instance, you may not put nums in order, which would be bad because you were not asked to modify the array.
@precondition: nums.length >= 2
Note: You will lose credit if you use a constant to represent the smallest or second smallest number. See pseudocode
| Method Call | return value/output |
| secondSmallest( { 2 , 18 , 22, 4 , 6 } ) | 4 |
| secondSmallest( { 3 , 7 , 15 , 1 ,101} ) | 3 |
boolean isPalindromic(int[] nums)
Description:This method returns true if the elements of nums are a palindrome.
| Method Call | return value/output |
| isPalindromic(( { 5 , 2, 7 , 2 , 5} ) | true |
| isPalindromic( { 5 , 2, 7 , 3 , 5} )) | false |
| isPalindromic(( { 1 , 2, 1} ) | true |
Old versions:
String 1 and Array 1 Exercises
Exercises for String 1 and Array 1 (no loops)
When you are done, you can copy and past the score() method below into your class. It will test some (but, by no means all) of the things that your code should do
Create a class called StrArr1 and add each method below into it.

For the absVals() method below use the Math.abs() Java method.
For the randos1to10() method below use the Math.random() Java method. Create a new array to store random integers. Each integer should be [1,10]