IB Exam Dates
May 19th and May 20th
Extra Credit-
For this quarter, the only available extra credit is to complete the extra IB exam 2010 (both Paper 1 and Paper 2) and this must be done by Monday May 18th, no later. Do not do the “Case Study” part. The case study is no longer part of the test .
Homework
Exams NOT yet done
- paper 2 of 2005 page 57 (paper 2, we think)
- 2006 ALL
MIS
- Monday the 18th :2014 paper 1 , 3 , 5 , 6, 13, 14
- Friday the 15th : Do any 5 questions from 2006 Paper 1 (Part I)
- Thursday the 14th : Do questions 12-15 of the 2006, paper 1 also in dropbox.
- Wednesday the 13th : 2013 paper 1 : 12, 14, 15
- Friday May 9th : Questions 1 and 2 from 2013 Paper 2
- Thursday May 8th : Questions 15 and 16 from IB 2008 Paper 1 (those last 2 questons)
- Wednesday May 7th : Ib 2008 paper 2, questions 1 and 2 (NOT 3 of case study) :
- Wednesday May 6th : Complete 2008 paper 1 in class. Begin 2008 Paper 2 .
- Two dimensional arrays: lesson
- Tuesday May 5th : 2008 IB Test up through and including question 14.
- Monday May 4th : Complete assigned questions from 2008 IB Paper 1. Questions 1 – 8 , completing the 2008 paper 1
- Friday May 1st: 2009 IB test, question 1 -13 (I will help with 2 and 9, skip 10, 12). Your answers must be on a separate sheet because you are handing them in.
- Thursday 30th :
- 1) complete the 2005 IB test
- 2) Research the answers to the following questions
- What is CAD software?
- What are CASE software tools? link 1
- Wednesday the 29th:
- 1) do questions 11 and 12 from IB test
- Tuesday the 28th : learn the following terms/research
- Monday the 4th : 1
- software feasibility report pptx (also in dropbox)
- answer the IB questions
- Question 1) What are some real world scenarios that this video uses to try to explain what MIS is (a little after 4 minutes)
- Question 2) After going over the personal example, what are some questions that an “organizational examples” of the types of questions that MIS asks and answers
NETWORKS
- Thursday 23rd: In class test on networks and terms (‘user defined method’), etc… I am going to ask you to re-answer the encapsulation problem from the last test, which no one correctly answered.
- Wednesday 22nd: 1) end of chapter questions 33-35 , 37, 42, 43-47, 48* ,49-63 . Look up what a “check sum” is and how it can be used to ensure the integrity in the transmission of data (2010 p1)
- Tuesday 21st: 1) Look up what a “user defined method” is. 2) end of chapter questions 1-6, 11 , 13-2-, 28, 29-32 .
- Monday 20th: Networking (book) cont’d. Read pages 495- end of chapter. be prepared for a check in quiz. How Tor works 1
- Friday : Networking (book). Read pages 488 – 495 . Make sure that you understand what a “data packet” is defined on page 495. Yes, there might be a “check in”
- Thursday : Complete IB take home exam. Research the pros and cons of “virtual memory”
- Wednesday March 15th : In class “quest” – an IB exam on OOP.
- OOP Stuff
- UML diagrams
- polymorphism
- overriding
- Tuesday March 14th : Comlete 2005 AP question #2 due before class Tuesday.
- Monday March 13th : Complete the bank runner class assignment . You do not need to implement the binary search method or the binary search algorithm or the sortByAccountId() unless you want extra credit. If you do indeed want extra-credit, then you must do sortByAccountId() before Monday.
- By end of Class Friday: complete : http://mrmonline.org/bank-account-inheritance-assignment/
- Friday March 9th : Complete Subshnu assignment
Thursday March 9th : Complete Subshnu assignment- Wednesday March 8th:
 Complete the highlighted methods from this assignment
Complete the highlighted methods from this assignment
March Break Homework
1) complete any final parts of your IA. I am uploading them the Monday of your return. Any work done after that will be too late
2) Read chapter 15 p.487-494
Objects in Java
Your IA is due for final grading on Monday the 9th
- Yup, Lin, that includes you too.
Chapter 10 p.333-
- Monday 3/2 : Hand in a ” Criteria for Success”
- Tuesday 3/4 : 10. 1 read p. 333-340
- Thursday 3/11: 10. 2 read p. 340-end of chapter
- Friday 3/12 Complete the Designing document, examples: link 1 , link 2 , link 3 . At least 1 flow chart is required. You can use this free web app to make a flow diagram.
- Monday 3/16- record of tasks like link 1 , link 2 , link 3
- Tuesday 3/17- end of chapter questions : p. 356 -7 , #1 -4 , #7,#8 , #9 , #14, #16 , #24-26 , #27 , #28
- Wednesday : download Hypercam or OBS and start videoing (due this Monday)
- Thursday – End of chapter questions #29, 30, *33-36*, 38-41
- Friday – #68, 72 homework questions. Work on the video
- Monday -Complete video of your project (see examples in our dropbox folder) Even if we have a snow day Friday,the video is due on Monday
- Tuesday -work on “Development-‘developing’ the product” 500-1000 words
- Wed quiz on Operating Systems chapter
- Thursday work on “Development-‘developing’ the product” 500-1000 words
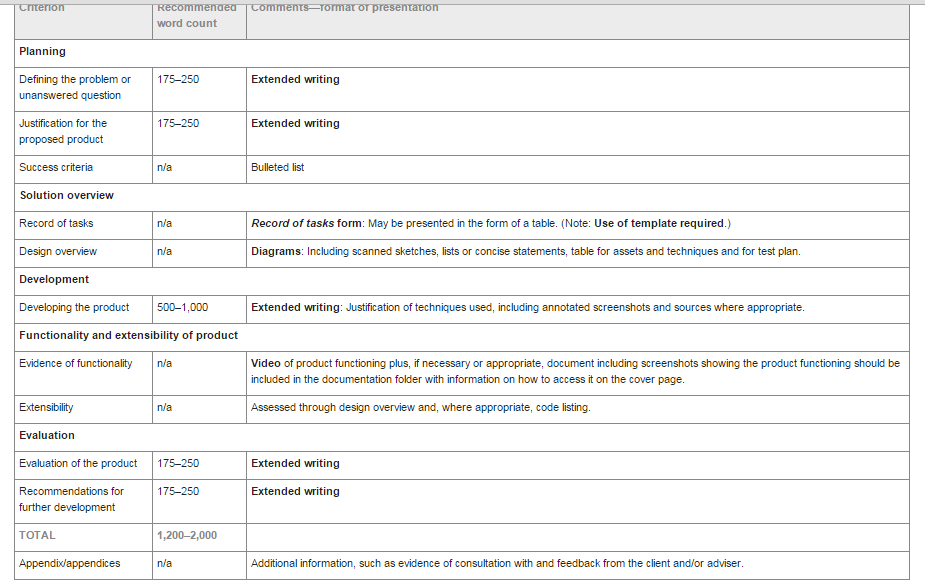
- Friday – “Development-‘developing’ the product” is due (should be printed out ,not emailed)
 Chapter 9
Chapter 9
- Due Tuesday 10th : read pages 285-290 (skim 291-294)
- Due Wed 11 th- : read p. 295-301 (here’s a link for compiler/interpreter also)
- explanation of managed vs unmanged code
- Thurs 12th : 301-310 , 316 (asynchronous)
- Friday 13th : Encapsulation (317-18), End of Chapter questions : 11-18 , 47-53
- Check in on IA on tuesday after break. You should be basically done.
- Wednesday : end of chapter questions p. 54, 55, 67 , 77 – 79 , Thought Questions 1,2
- Thursday: Quiz on Chapter. also on quz: beta testing and alpha testing
- Friday: Hand in a ” Rationale for Proposed Solution” (this, if you recall, is the second written part of your IA)
- IA Link
Back to IB SL main page.
Chapter 7
- Due Tuesday the 20th : Read chapter 7.1 Pages 195-203
- Due Wednesday 21st: Read 7.3 page 210-214
- Due Thursday 22nd. Ready 7.7, p.232-235
- Due Friday 23 rd : End of chapter questions, # 7- 10, 11-15 ,
- Midterm week :
- Wed the 2nd : End of chapter questions, # 51, 56, 58 a , 58 b,
- Wed the 2nd : Begin chapter 9 pages 286-287 ,
- Test on chapter 7 will be on Friday February 6th
Chapter 6
- Monday 1/5 . Read pages 167-178
- Tuesday 1/6 . Finish chapter (179-186)
- Next IB Project Check Thursday January 15th. This means that you should be using class time and homework to achieve the goals we set. Yes, including Friday when I will not be in class (due to a field trip). I am assuming you are using homework time and also class time, and not assigning homework
- Wednesday January 14th Read pages 195-205. We need to know pseudocode!
-
Thursday January 22nd: Friday January 16th Chapter Test More here
[redact]
Thursday January 15th, Wednesday January 14th End of the chapter questions 21-30, 40,- Thursday, January 15th End of the chapter questions 59
- Thursday January 22nd: Monday January 19th Chapter Test
[/redact]
Winter Break Assignments
Reading and End of Chapter Questions for All Students
1) Read pages 151-167. When we get back from break, we will see Ricky’s Powerpoint on this topic
Your IA project
|
Senoirs
Complete the project in full and submit on Monday of return |
Non Seniors
Have a working prototype that demonstrates
- UI for app (doesn’t have to be finished)
- basic code base that
- performs original programming
|
Tuesday 12/23: Senior teachers
Monday 12/22 : Completed Draft of powerpoint. Seniors: We are sitting down to look at IB project
Friday 12/19 : completed draft of powerpoint is due. . Hand in Your Rough draft for “Criteria for success”
Thursday 12/18 : Hand in Your Rough draft for “Rationale for solution” . Minimum of 200 words
Wednesday 12/17 : Hand in Your Rough draft for “Defining the problem” Minimum of 200 words, yes this is graded .
Chapter 5 Test: Tuesday the 16th
Monday 12/15 : TBA
Friday 12/12 : Rough Draft #2 (and last rough draft) emailed by end of period (5 points)
Thursday 12/11 : End of Chapter Questions 53-end
Wednesday 12/10 : End of Chapter Questions 43-52
Tuesday 12/9 : End of Chapter Questions 30-42.
Monday 12/8 : End of Chapter Questions #17-22, 24-30
Powerpoint 1st draft due -end of class Friday 12/5 First draft should be a minimum of 5 slides with content.
Complete chapter before Thursdays’s class
Thanksgiving Break homework
1) Read pages 119 – 134 (You don’t need to read Magnetic disks)
Good Youtube Videos on CPU/ALU
Powerpoint Projects
Each of you will be responsible for creating a powerpoint project . Cover all topics and key vocabulary in the book. Your powerpoint should probably be 10-15 slides. It should include images and, if possible, any good videos that we can watch.
Powerpoint guidelines
- visible text (no dark text on dark background)
- keep the wording as little as possible
- rule of thumb: If it’s too much text for audience to read, then it shouldn’t be there. Instead you should summarize key points with text and say out loud the extra info and details
- animations/visuals are always the best way to go
|
These must be completed by
| topic |
Student |
| Advanced Logic Gates |
David Sullivan |
| Arithmetic Logic Unit/ CPU/Input Output/fetch execute and parallel hardware (a link) |
Amr |
| Secondary Storage Devices + RAM/ROM (133-140) |
Jacob |
| Unit 6 |
|
| Information Systems (chapter 12) |
Scott Robertson |
| Composite Variables (7.3) + Searching and Sorting Algorithms (selection, insertion, binary search, linear search -see chapter 7) |
H. Kim |
| Machine Language/assembly language (6.2,6.3, 6.4) (a link) |
Ricky H |
| Networks Chapter 15 |
Dom R. |
| File Systems (see chapter 11) |
Misha |
| Information Systems (chapter 12) |
Brian L |
| The World Wide Web (ch. 16) |
B. Struhl |
| Operating Systems (all of chapter 10) |
Johansen |
Chapter 4: Gates (p.91 – 117)
You are responsible for most, but not all , of the contents in this chapter.
Logic Gates QUIZ on A on Wednesday the 26th
- truth tables to Gate(s)
- Write truth table based on gates
- definitions from reading
- end of chapter questions p. 112-116 #15-31, 34, 46 – 48 , 69, Answers to these of the chapter questions are in dropbox in the “chapter 4” folder
Topics Not covered on the IB
- symbols for gate types (instead the word ‘and’ will appear in a bubble) such as
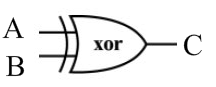
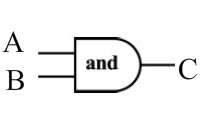
- Read and understand/know the following page and their topics
- Assignment #1 Due Tuesday 11/18
- p. 92
- 94 – 98 ( but with IB symbology)
- transistors (99 -100)
- Circuit definitions (bottom paragraph of 101)
- Assignment #2 Due Wednesday 11/19
- 4.5 Circuits as Memory, p. 108-9
- 4.6 Integrated Circuits (p.109-110)
- You do *not* seem to need to know adders, half adders, multiplexers or gates with more than 3 inputs
Seniors : Large grade: Friday the 21st,
- server should run on local computer in the lab so that we can look at it, together.
- approx 25 points focusing on
- use of php/mysql
- how data is saved
- use of sessions (if applicable)
- logging in (if applicable)
- how code is organized (use of modular design)
- design/menus for navigation
Grading Rubric:
Objects in Java
2 Dimensional Arrays
Chapter 3 (Week of 10/6-10/13). You can also read the powerpoint which is in the class_notes folder i-n the ‘chapter_3’ folder.
- Test : Wednesday 10/29
Friday 10/25 (Date moved to maximize Lynda.com access use)on
- chapter 3 on all vocabulary, terms concepts in reading.
- powerpoint in dropbox
- chapter_3 end of chapter questions (skip 35-43)
- Array Fun 1
- Required CodingBat Problem
- Array Fun 2 due approximately 10/25
- Any 20 from Array 2 at coding bat due approximately 10/20
- Due Friday 10/15 : Complete the end of the chapter questions on pages 84-89 and check your answers against the key in the dropbox folder. Come in with any queries about the questions.
- Due Wednesday 10/15 : 73-83 Be prepared for a check in quiz on your reading.
- Due Thursday 9th, : Read p.53-73. You are responsible for becoming familiar with all the vocabulary, terms and the pros/cons of the various types of technologies explained. .
- ArraysInMemory_version3
- Some test cases for validate form
- Monday 10/6 : Validate Form project
- Test :
Tuesday Wednesday 10/6 on Strings, decimal point to binary conversion, 2’s complement
- Programming concepts. Primitives vs Strings
- Friday 9/19
Tuesday 9/15 : Non decimals numbers quiz/test. On
- converting between decimal, binary, hex and any arbitrary base.
- on shortcut for going between bases 2,8 and 16
- on adding/subtracting numbers in different bases
- You can use this tool to help test your understanding of binary/hex
- converting decimals like 21.25 to binary (**new) p. 63-66 in book
- bit, byte , word p. 45
- 2’s complements
- Java number types
- Run the following code, what’s going ?
|
|
byte x = 127; byte y =3; byte sum = x + y; System.out.println(sum); |
- Monday 9/15 : read p.53-67 2’s complement and negative numbers and number overflow
- Friday 9/12 : Complete the questions in dropbox in “ch 2” folder.
- Do questions
- 7-9
- 13-22
- 31-37
- 39 -41
- 44-46
- 63-68
- 75-76
- 80-119 (A lot of practice, here for converting decimal numbers to other bases )
- Short Quiz on Friday 9/12: on converting decimal numbers to other bases .
- 9/11 : read page 45 .
- 9/10 : quiz on four generations of computer hardware.Be familiar with the hardware items, their properties/traits as well as pros/cons and be able to classify which generation each belongs to. I added a powerpoint to the dropbox folder that supplements textbook reading.
- 9/7 : Read all of chapter 1 by Monday the 7th of September. Answer all end of the chapter questions by the Tuesday the 8th. I hope it’s obvious that you should not write in the book.