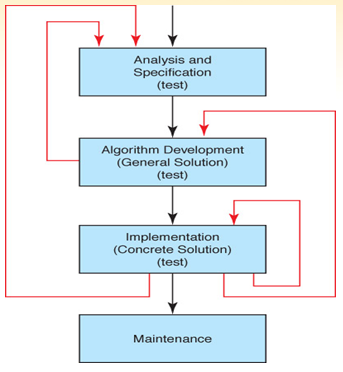
A PlayList project will be based on Three Classes
The Artist class will store core information about an artist
The Song class will store basic information about a music song
The PlayList class will manage lists of songs and artists
Artist
- Constructor(s) :
public Artist( String name) { //missing code }
- Instance Variables (“global” variables)
|
|
private String artistName ; private Song[] songs ; - an array storing the songs of this artist |
Methods
|
|
private int indexOf(String songName) // returns index position of parameter in the array public void addSong(Song song) public void removeSong(Song song) public void removeSongByName(String songName) public Song[] getSongs() //returns songs array public String getName() // returns artistName |
Song
Constructor(s):
|
|
public Song(String songName, Artist artist){ //missing code } |
Instance Variables
|
|
private Artist artist ; public String songName ; public long date //(date added to list) |
example of how to get current milliseconds as a long
Method
|
|
public Artist getArtist() |
Artist
Song
PlayList
PlayList
- Instance Variables
-
private String listName : This is the ‘name’ of your playList
-
private Song[] songs;
-
private int[] stars ; //how many stars each song has between 0 and 5 inclusive.
- Note: songs and stars are parallel Arrays
- Constructor
-
public PlayList(String name) : There should be only 1 constructor that takes a parameter representing the name of the playList
- Accessor Methods
-
public double averageRating() // returns the average star rating for the list
-
public double averageRating(Artist artist) // returns the mean star rating associated with artist
-
public Song[] getSongs(Artist artist) // returns an array populated by the songs of the parameter artist
-
public Song[] getSongs() // returns all the songs in the list
Mutator Methods
-
public void swap(Song song1 , Song song2 ) // switches positions of these two (maintain parallelism!)
-
public void add(Song song , int stars)
-
public void removeSong(Song song, String artist ) //removes song associated with artist
- Note: Be careful here. You are allowed to add the same song and artist. Duplicates are allowed.
-
public void removeArtist(Artist artist ) //removes all elements associated with artist
-
public void removeLowStars(int cutOff) //removes all elements associated with a star rating less than cutOff
-
** public PlayList sortByDate() //this returns a rearranged PlayList based on each Song’s date
-
** public PlayList sortByRating() //this returns a rearranged playlist so that the 5 starred elements are the first group in the list, 4 stars second …1 stars, last
-
** public PlayList shuffle() //this returns a new PlayList in which all of the songs have been reordered randomly.
Artist
Song
PlayList
 http://
http://