Tag Archives: loops
String Loop Assignments [Java]
Write the body for the methods described below.
Tester File here (This one does not yet test the newest method)
As always, do not import any external libraries. All of the coding can be accomplished by using just loops, arrays, strings and variables. Using anything else will lead to total loss of credit on associated methods.
Once you have completed each method, copy and paste the code in this file into your class. Then run the test() method and you will get feedback on your code. Note: This does not test all the methods. I have added new methods since writing that tester file. Also, please make sure that:
- all methods are spelled/capitalized exactly as shown on this page
- variables are camelcase and have meaningful names
- for i loops use i as a variable
- for-each loops do not use i as the variable
For each method below, you can assume that the parameters are not null
Part I
boolean isAfterN(String str, String chrs, int index)
Description: This method returns true if chrs appears in str after index .
@precondition: index + chrs.length() < str.length()
int countF(String str)
Description: This method returns the number of times that the the lower case letter ‘f’ occurs in str .
| Method Call | return value/output |
| countF(“abcdef”) | 1 |
| countF(“abcdfef”) | 2 |
| countF(“fff”) | 3 |
| countF(“xxx”) | 0 |
boolean hasN_Fs(String str, int n )
Description: This method returns true if str has exactly n occurrences of the letter ‘f’ in it.
String threeTimes(String str)
Description: This method returns the String str concatenated with itself three times
| Method Call | return value/output |
| threeTimes(“foog”) | “foogfoogfoog” |
| threeTimes(“abc”) | “abcabcabc” |
| threeTimes(“zt”) | “ztztzt” |
| threeTimes(“”) | “” |
String nTimes(String str, int n)
Description: This method returns the String str concatenated with itself n times
| Method Call | return value/output |
| nTimes(“fg” , 2 ) | “fgfg” |
| nTimes(“abc” , 0 ) | “” |
| nTimes(“zt” , 3 ) | “ztztzt” |
| nTimes(“uiz” , 4 ) | “uizuizuizuiz” |
int countMiddleChar(String str)
Precondition: str.length() ≥ 3.
Description: This method returns the number of times the middle letter of str appears in str.
| Method Call | return value/output |
| countMiddleChar(“acbcb” ) | 2 |
| countMiddleChar(“acbcx” ) | 1 |
| countMiddleChar(“bbbbb” ) | 5 |
| countMiddleChar(“xytbtzy”) | 1 |
int indexOf(String haystack, String needle)
Description: Write your own indexOf() method. Just to avoid any confusion – you cannot make use of the String’s built in indexOf() method. Our method returns the index of the 1st occurrence of needle in haystack . (Full credit if you can get this to work with Strings whose length is greater than 1).
int countChars(String str, String chars)
@precondtion : chars.length() <= str.length()
Description: This method returns the number of times that chars occurs in String str .
| Method Call | return value/output |
| countChars(“momdadmom” , “dad” ) | 1 |
| countChars(“foobofoo” , “foo”) | 2 |
| countChars(“foobofoofoo” , “foo”) | 3 |
| countChars(“foobofoofoo” , “xy” ) | 0 |
Part II
String[] toArray(String str)
Description: This method returns an array comprised of the individual characters of str
| Method Call | return value/output |
| toArray(“abc” ) | { “a”, “b”, “c”} |
| toArray(“xyz” ) | {“x”, “y”, “z”} |
String[] toArraySansChar(String str, char ch)
Description: This method returns an array of Strings comprised of single letter strings extracted from the input String str ; however, we will always skip the char ch :
|
1 2 |
char c = '3'; String s = String.valueOf(c); |
String[] reversedBy2s(String str)
Description: This method returns an array of Strings comprised of pairs of characters from the input, — in reverse order as shown below:

String reverseBy3s(String str)
Description: This is like the prior method, except you are going by 3’s and returning a String , not an array of Strings.
boolean isPalindrome(String str)
Description: This method returns true if str is a palindrome
| Method Call | return value/output |
| isPalindrome(“abc” ) | false |
| isPalindrome(“aba” ) | true |
| isPalindrome(“abba” ) | true |
Array Fun 1 [Java]
Array Fun 1
Create a Class called ArrayFun that has the following methods Write the body for the methods described below.
public int[] swapFirstLast(int[] nums)
Description: This method returns a new version of the array with the first and last elements of
numsswapped.
| Method Call | return value/output |
| swapFirstLast( {3, 2 ,5 } ) | {5,2,3} |
| swapFirstLast( {7, 6 ,9 ,12} ) | { 12 , 6 , 9, 7} |
public String[] swapFirstMiddle(String[] strs)
Description: This method returns a new version of the array with the first and middle elements of
strsswapped.
| Method Call | return value/output |
| swapFirstMiddle( {“a”,”b”,”c” } ) | { “b”, “a”, “c”} |
| swapFirstMiddle( { “zoo”,”foo”, “xoo”} ) | { “foo”,”zoo”, “xoo”} |
Loops
public void printEveryOther(int[] nums)
Description: This method prints every other element of
numson new lines .
| Method Call | return value/output |
| printEveryOther( {1 , 2 , 3 , 4 } ) | 1 3 |
| printEveryOther( {13 , 42 , 33 , 44 , 52} ) | 13 33 52 |
public int sum(int[] nums )
Description: This method returns the sum of
nums..
| Method Call | return value/output |
| sum( { 2 , 8 }) | 10 ie 2 + 8 |
| sum( { 2 , 8 , 4 } ) | 14 ie (2 + 8 + 4 ) |
public int sumOdds(int[] nums )
Description: This method returns the sum of all the odd element of
nums.
| Method Call | return value/output |
| sumOdds( { 5 , 2, 4 , 6 , 7 } ) | 12 ( ie 5 + 7 ) |
| sumOdds( { 13 , 3, 2, 6 , 7 } ) | 23 |
Description: This method returns the mean of
nums. Pay close attention to the second sample call and make sure you get “5.25“
| Method Call | return value/output |
| mean( { 2 , 8 }) | 5.0 ie (2+8)/2 |
| mean( { 2 , 8 , 4 , 7 } ) | 5.25 ie (2+8+4+7)/4 |
public double largest(double[] nums )
Description: This method returns the element of
numswith the greatest value. Make sure that you test out the second call and get ‘-2‘.
| Method Call | return value/output |
| largest( { 2.6 , 8.2, 5.2}) | 8.2 |
| largest( { -2,-11, -4} ) | -2 |
public int sumEveryN(int[] nums, int n)
Description: This method returns the sum of every
nelements ofnums..
| Method Call | return value/output |
| sumEveryN( {1 , 2 , 3 , 4 }, 2 ) | 4( ie 1 +3) |
| sumEveryN( {13 , 42, 15, 33 , 44 , 16 , 52} ,3) | 98 ( ie 13 + 33+ 52) |
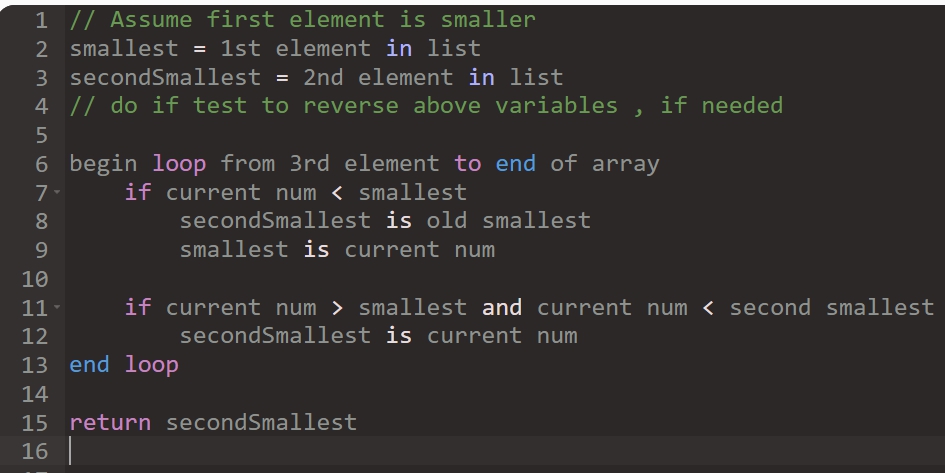
*public int secondSmallest(int[] nums )
Description: This method returns the element of
numswith the second smallest value.
| Method Call | return value/output |
| secondSmallest( { 2 , 18 , 22, 4 , 6 } ) | 4 |
| secondSmallest( { 3 , 7 , 15 , 1 ,101} ) | 3 |
** boolean isPalindromic(int[] nums)
Description:This method returns true if the elements of
numsare a palindrome..
| Method Call | return value/output |
| isPalindromic(( { 5 , 2, 7 , 2 , 5} ) | true |
| isPalindromic( { 5 , 2, 7 , 3 , 5} )) | false |
| isPalindromic(( { 1 , 2, 1} ) | true |
1 < base < 11@precondition
num1.length = 5 and num2.length = 5@postcondition: the returned array has 5 elements representing the sum or an ArithmeticException is thrown
Description: This method attempts to replicate addition. Consider both num1 and num2 represent the five digits of a number. Each element in the array stores one of the digits. For instance, the number 143 would be represented as {0,0,1,4,3 }. Numbers can be in any base between 2 and 10 inclusive , and the number 101102 in binary would appear in an arrays as : {1, 0, 1 , 1, 0 } . Let’s assume the numbers are positive. You should return an array representing the digits of the sum of num1 and num2. You may not do any math besides addition. You may not use any external libraries for any math or base conversions. If the number of digits in the sum exceeds the maximum number of digits (5) , you should throw an arithmetic exception as shown in the code below:
Note: You may not use any kind of helper or utility methods that are built into pre-defined Java classes for converting numbers between bases. Only use techniques taught in this class. What you have to do is reproduce the additional algorithm and find a way to carry digits , programmatically.
| Method Call | return value/output |
| add( {0,0,0 ,4,2},{0,0,0,5,1}, 10) | {0, 0, 0, 9, 3} ie (42 + 51 = 93) |
| add( {0, 0, 0 ,7,2},{0,0,0,5,1}, 10) | {0, 0 , 1 , 2, 3} ie (72 + 51 = 123) |
| add( {0, 0 , 0 , 1 , 1}, { 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 }, 2) | {0, 0 , 1 , 0 , 0} ie ( 112 + 12= 1002 ) |